Several factors can increase the risk of developing venous thrombosis. Here are the most relevant:
- Prolonged immobility:
Long journeys, hospitalizations, or bed rest can reduce blood flow in the legs and promote the formation of blood clots. - Surgeries and Trauma
Surgical procedures, especially orthopedic ones (such as hip or knee replacement), and fractures increase the risk of DVT.
3. Coagulation Disorders
Some people are born with genetic alterations that cause their blood to clot more easily, even without an obvious cause.
4. Pregnancy and Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal changes during pregnancy or the use of oral contraceptives can alter blood clotting.
5. Cancer and Oncological Treatments
Tumors, chemotherapy, and certain medications directly affect the coagulation system.
- Obesity and Smoking
Both factors impair circulation and increase blood viscosity, raising the risk of blood clots.

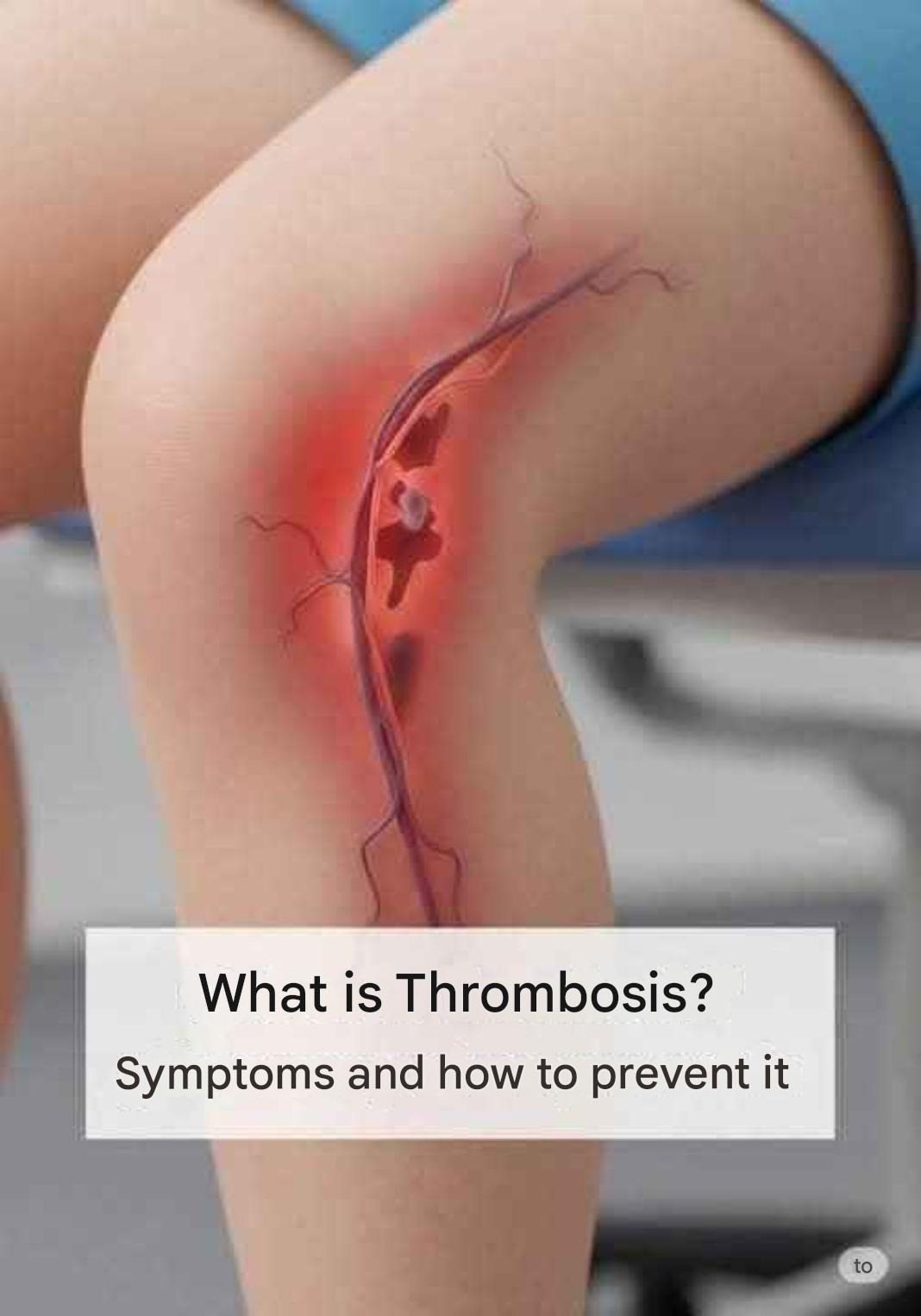
In many cases, venous thrombosis is asymptomatic, which makes being informed even more important. But when symptoms appear, it’s crucial to act immediately. Some of the most common are:
Swelling in one leg (especially the calf),
pain or tenderness to the touch,
a feeling of warmth or burning in the affected area,
changes in skin color (redness or bluish tint),
and visible or dilated veins are all