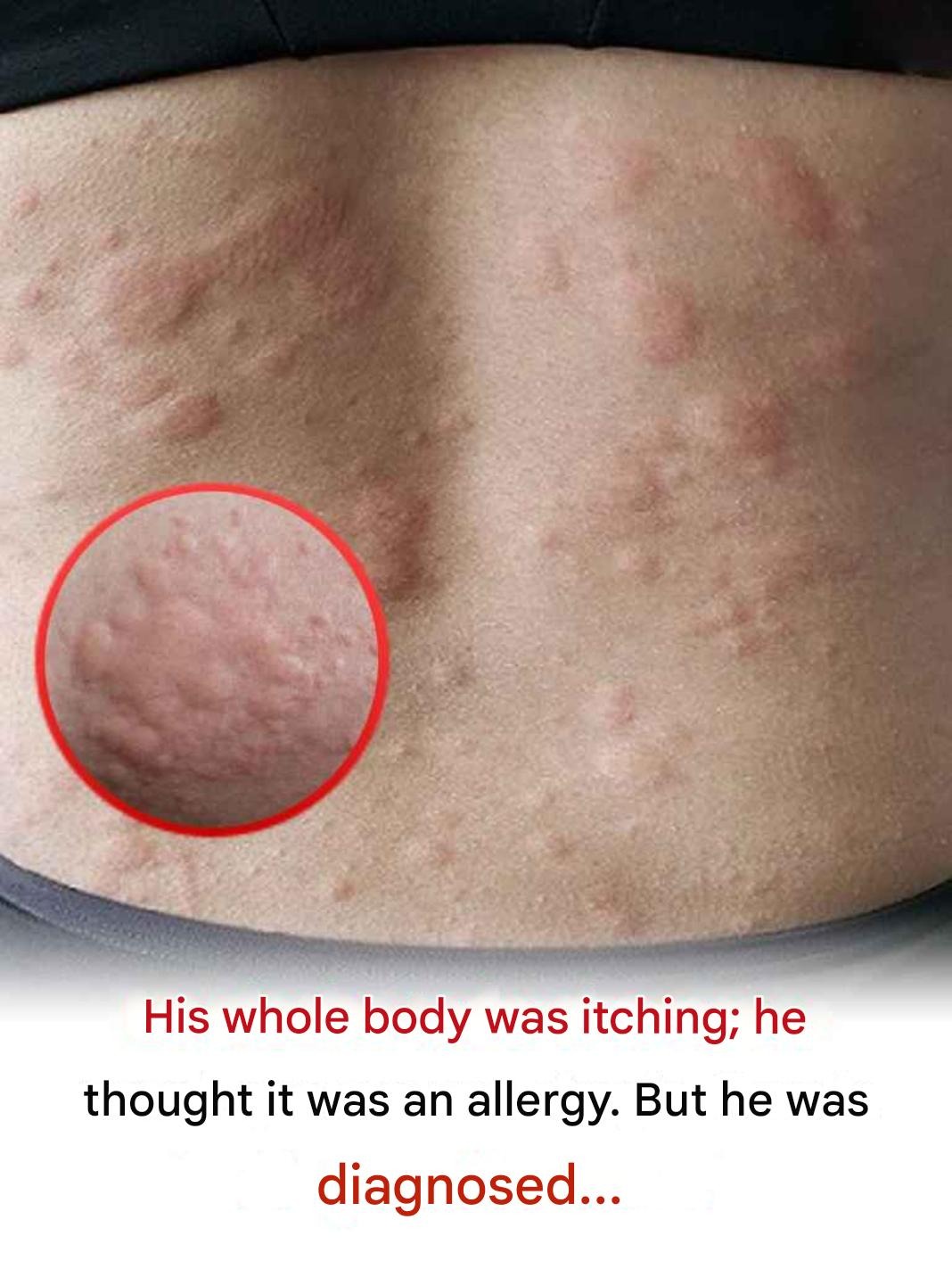
The appearance of hives, which can appear anywhere on the body.
– Hives that may be red, purple, or skin-colored, depending on skin tone.
– Hives that vary in size, change shape, and appear and disappear repeatedly.
– Itching, also called pruritus, which can be intense.
– Painful swelling, called angioedema, around the eyes, cheeks, or lips.
– Outbreaks triggered by heat, exercise, or stress.
– Symptoms that persist for more than six weeks and recur frequently and at any time, sometimes for months or years.
How to find relief: Treatment options
The first step in receiving treatment is determining whether you actually have hives. In most cases, a doctor can determine if you have hives through a physical exam. Your skin will show signs of the welts associated with urticaria.
A doctor might also perform blood tests or skin tests to determine the cause of the hives, especially if it resulted from an allergic reaction.
If you experience a mild case of hives unrelated to allergies or other conditions, you may not need prescription treatment. In these circumstances, a doctor might suggest temporary relief through: