Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or smokeless tobacco significantly increases the risk of developing oral cancer. About 80% of oral cancer cases are related to tobacco use.
Excessive alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol in large quantities increases the risk, especially when combined with tobacco use.
Human papillomavirus (HPV): Certain strains of the HPV virus, particularly HPV-16, have been linked to an increased risk of oral cancer.
Poor diet and nutrition: A diet lacking essential vitamins and nutrients, especially fruits and vegetables, can increase susceptibility to oral cancer.
Age: Oral cancer is more common in older adults, particularly those over 50.
Family history: A family history of cancer can increase the likelihood of developing oral cancer.
Stages of oral cancer:
Oral cancer progresses in stages, which helps determine the extent of the disease and guide treatment decisions. These stages include:
Stage 1: The tumor is less than 1 inch and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 2: The tumor grows to between 1 and 2 inches, but remains localized and has not spread to lymph nodes.
Stage 3: The tumor is larger than 2 inches and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, but not to other parts of the body.
Stage 4: This is the most advanced stage, where the cancer has spread to surrounding tissues or other parts of the body, including distant organs.
The stage of cancer helps determine appropriate treatment options and also provides an indication of the prognosis.
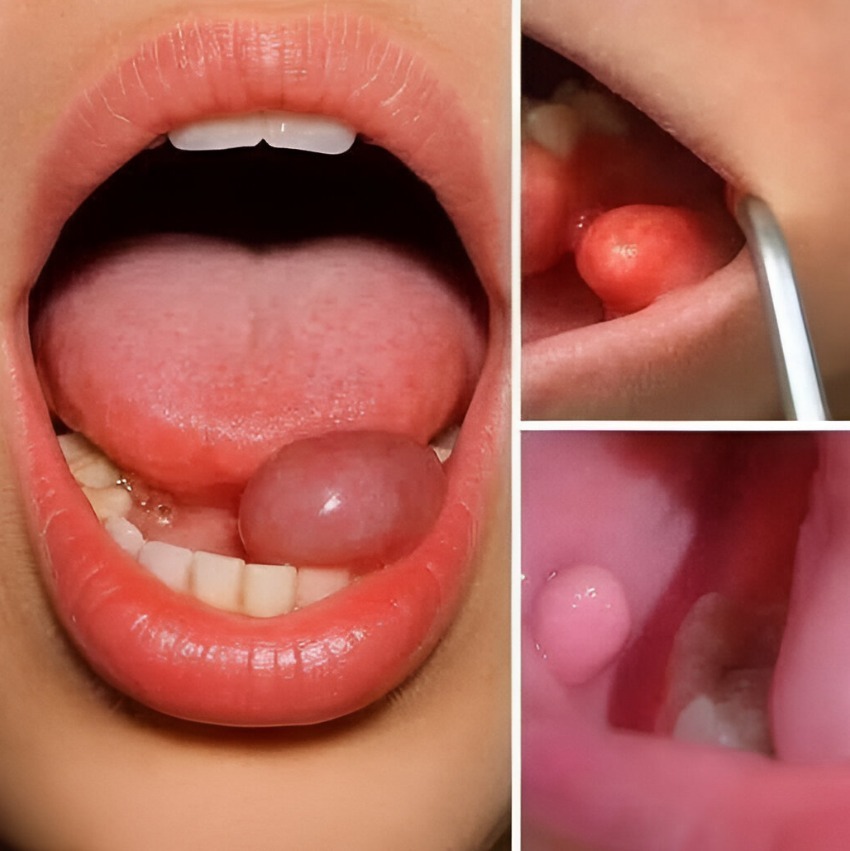
The best homeopathic treatments for canker sores in 2023.
Treatment for oral cancer:
Oral cancer can be treated with a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on the size, location, and stage of the cancer.
Continued on the next page