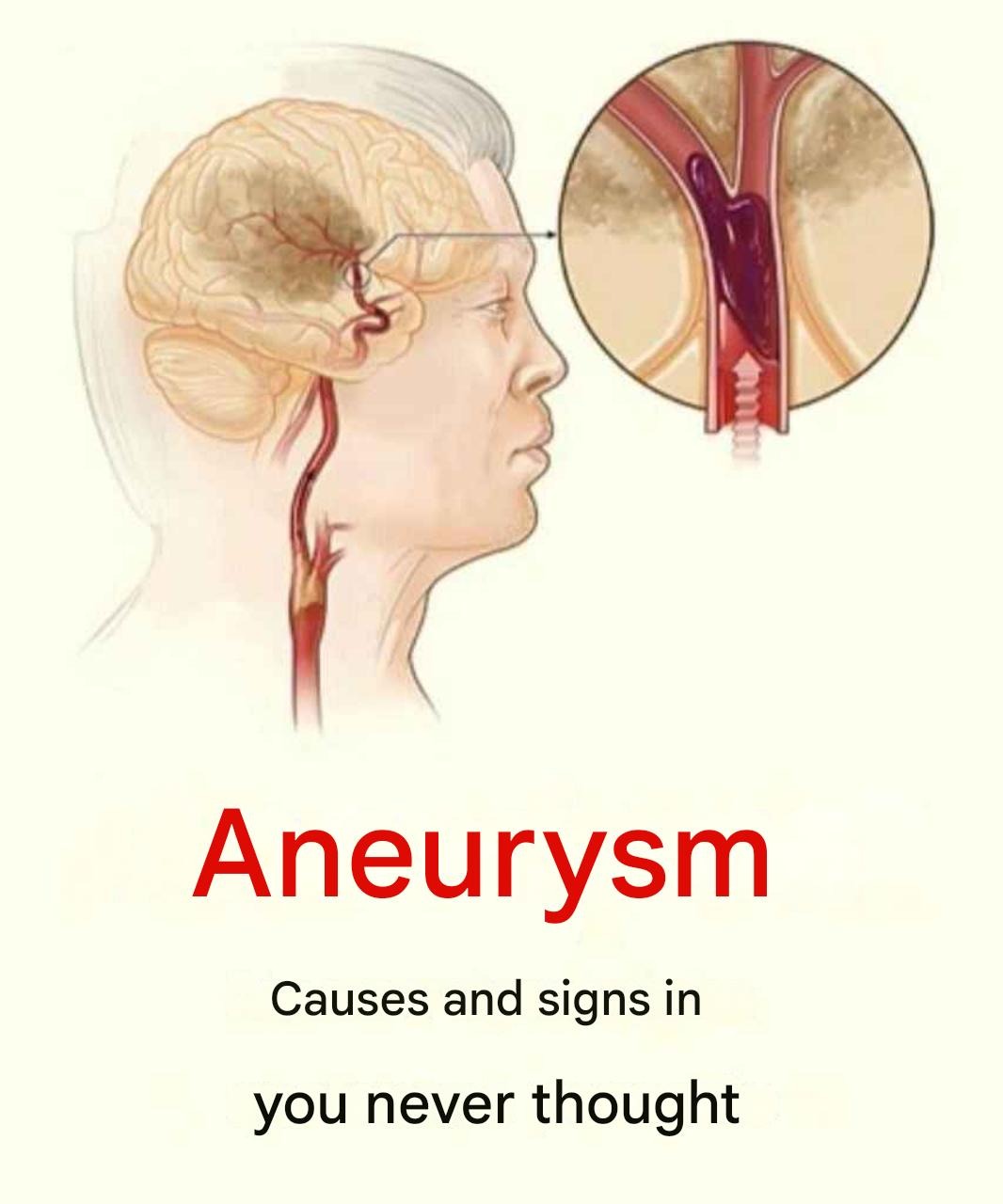
How to identify the early signs and symptoms of a stroke
With this knowledge in hand, you will be better prepared to face this medical emergency and help save a life.
If someone is suspected of having a stroke, it is essential to perform the SAMU exam, which consists of the following steps:
S (smile): Ask the person to smile. During a stroke, one side of the face may not move properly, resulting in an asymmetrical smile.
A (hug): Ask the person to raise both arms as if they were going to give you a hug. In the case of a stroke, one arm may not move or may fall off.
M (music): Ask the person to sing a song. A stroke can make speech difficult, resulting in slurred speech.
U (urgent): If the person cannot perform these actions, immediately call SAMU at 192.
People who have suffered a stroke are often unable to perform these tasks. If this happens, it is vital to place the victim on their side in a safe location and call emergency services (192). Observe whether the victim is still breathing normally. If breathing stops, begin CPR.
Symptoms of a Silent Stroke:
The main signs of a silent stroke, or microangiopathy, include progressive memory loss without affecting daily functions, difficulty or inability to walk, and changes in speech. Microangiopathy is a progressive vascular disease caused by small lesions in the brain, which affect its function.
Stroke symptoms in women
In addition to the classic symptoms of stroke, stroke in women may present with additional symptoms, such as:
General weakness.
Hallucinations, mental confusion, agitation, or disorientation.
Difficulty breathing or hiccups.
Seizures.
Loss of consciousness or fainting.
If you experience these symptoms, it is essential to go to the emergency room immediately or call SAMU at 192 to begin treatment as soon as possible.
Possible consequences of a stroke
The main impacts of a stroke include neurological deficits, difficulty communicating or understanding instructions, problems walking, dressing or eating without help, changes in alertness or even going into a coma.
The aftereffects can be temporary or very serious, varying according to the severity of the stroke, the region of the brain affected and the type of stroke, whether ischemic or hemorrhagic.
Ischemic stroke, stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, stroke treatment, post-stroke rehabilitation, stroke symptoms, stroke prevention, stroke causes