Gout is often associated with drinking too much or not eating healthily enough, but research suggests genetics play more of a factor in developing the arthritic condition than previously thought.
A recent study, carried out by an international team of scientists, looked at genetic data collected from 2.6 million people across 13 different cohorts of DNA data. That number included 120,295 people with “prevalent gout”.
By comparing the genetic codes of the people with gout against the people without, the team found 377 specific DNA regions where there were variations specific to having the condition – 149 of which hadn’t been previously linked to gout.
While lifestyle and environmental factors are certainly still in play, the findings suggest genetics play a major role in determining whether or not someone gets gout – and the researchers think there may be more undiscovered genetic links still to be found, too.
“Gout is a chronic disease with a genetic basis and is not the fault of the sufferer – the myth that gout is caused by lifestyle or diet needs to be busted,” said epidemiologist Tony Merriman from the University of Otago in New Zealand, when the study was published last year.
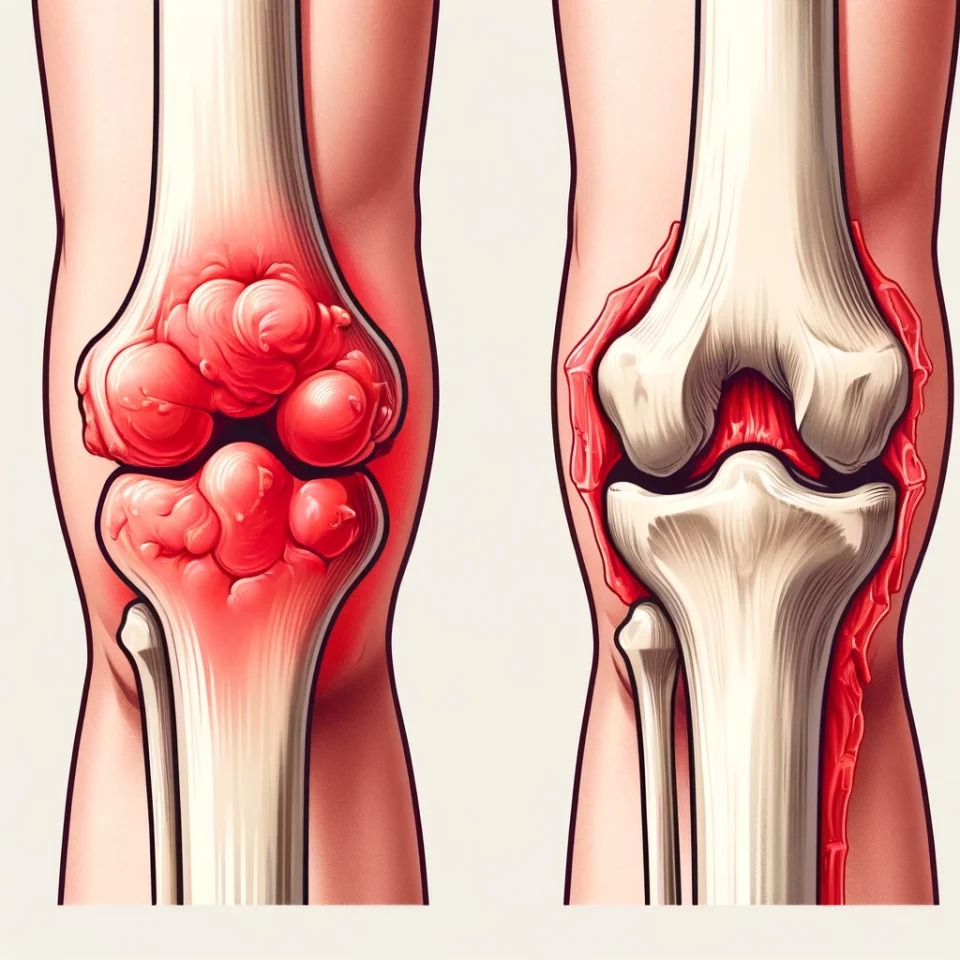
Gout takes hold when there are high levels of uric acid in the blood, which then form sharp crystal needles in the joints. When the body’s immune system starts to attack those crystals, it leads to significant pain and discomfort.